What is a Green Roof System?
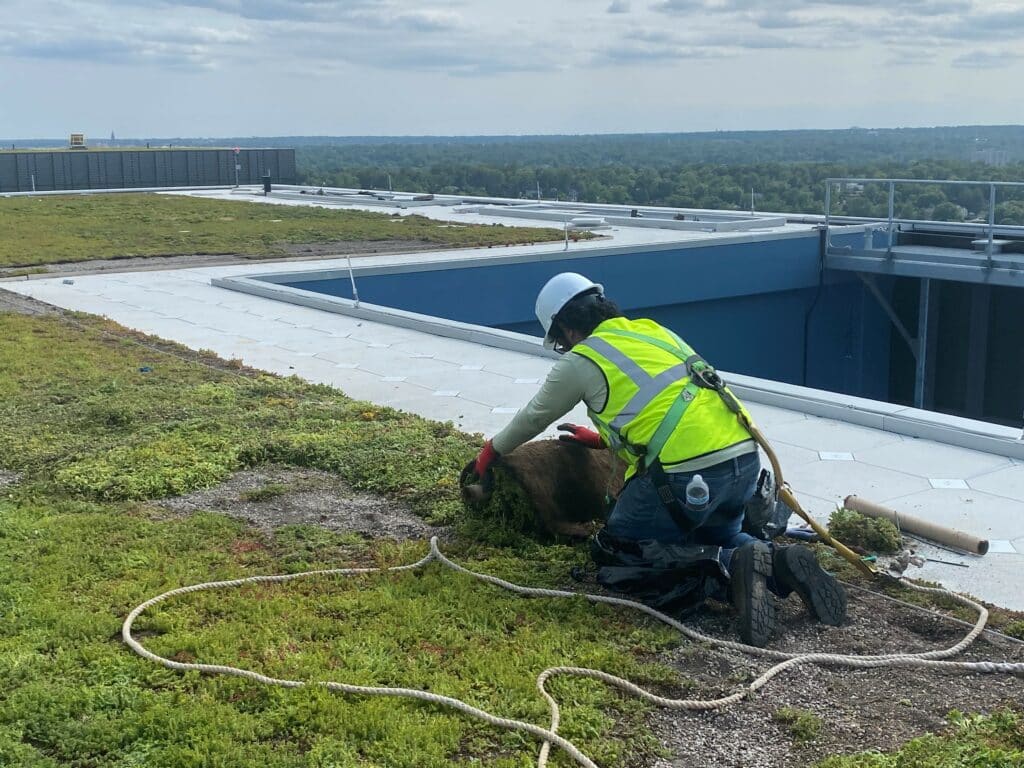
A green roof system is an innovative roofing solution that integrates vegetation and soil over a waterproof membrane on a building roof. Unlike traditional roofs, a green roof not only protects the structure beneath but also provides a host of environmental, social, and economic benefits. Green roofs can be classified into two main types: extensive and intensive. Extensive green roofs are lightweight, require minimal maintenance, and typically host low-growing vegetation such as sedum or moss. Intensive green roofs, on the other hand, are more elaborate, capable of supporting a wider variety of plants, shrubs, and even small trees, resembling a rooftop garden. These systems involve several layers, including a waterproofing membrane, root barrier, drainage system, soil substrate, and vegetation, all working together to enhance roof performance. Historically, green roofs have been utilized in Europe and Asia for centuries, and their adoption in modern architecture continues to grow due to urban sustainability efforts. By installing a green roof system, buildings can contribute to reducing urban heat, improving air quality, and enhancing overall city aesthetics.
Components of a Green Roof System
A well-functioning green roof system relies on multiple layers, each with a specific purpose to ensure plant survival and structural protection. The waterproof membrane protects the building from water penetration, while the root barrier prevents roots from damaging the underlying structure. The drainage layer ensures that excess water does not accumulate, maintaining optimal moisture levels for the plants. Above the drainage layer lies the growing medium, a specialized soil mix that supports plant growth while remaining lightweight. Vegetation is the visible layer that provides environmental benefits, from cooling the roof surface to attracting pollinators. Optional features, such as irrigation systems, sensors, and insulating layers, can enhance performance and reduce maintenance needs. Choosing the right materials for each layer is essential, as durability and efficiency directly impact the longevity of the green roof system. Modern innovations, such as modular green roof trays and lightweight soil substitutes, make installation easier and more adaptable to various building types.
Benefits of Installing a Green Roof System
Green roofs provide a wide range of benefits that extend beyond aesthetics. Environmentally, they help reduce urban heat island effects by cooling surrounding areas, improving air quality, and managing stormwater runoff. Economically, they increase property value, lower energy costs through improved insulation, and reduce the frequency of roof repairs by protecting the underlying structure. Socially, green roofs offer spaces for recreation, relaxation, and community engagement while promoting biodiversity in urban areas. Health benefits are also notable, as access to green spaces has been linked to reduced stress and improved mental well-being. Green roofs contribute to climate resilience by managing rainfall and controlling temperature fluctuations on building surfaces. They also encourage sustainable urban development, aligning with city planning initiatives that prioritize eco-friendly infrastructure. Implementing a green roof system demonstrates a commitment to environmental stewardship while enhancing the functionality and value of a building.
Design and Installation Considerations
Designing and installing a green roof system requires careful planning to ensure safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. A structural assessment is essential to confirm that the building can support the additional weight of soil, plants, and water. Plant selection is crucial and should consider local climate conditions, seasonal changes, and desired maintenance levels. Proper drainage and irrigation planning are vital to prevent waterlogging or plant stress. Collaboration with architects, engineers, and horticulturists can ensure that the design is both visually appealing and structurally sound. Local building codes and regulations should be reviewed, as some municipalities offer incentives for green roof installations. Common challenges, such as improper soil depth or inadequate drainage, can be avoided with proper planning and expertise, ensuring a long-lasting and successful green roof system.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maintaining a green roof system requires regular attention to sustain plant health and structural integrity. Routine tasks include weeding, fertilizing, monitoring soil moisture, and checking the irrigation system. Seasonal maintenance, such as preparing for winter or replacing damaged plants, is also necessary. Components of the system, like drainage layers and waterproof membranes, should be inspected periodically to prevent leaks and water accumulation. Lifespan varies depending on the quality of materials and maintenance practices, but with proper care, a green roof system can last decades. Tools such as soil moisture sensors, weather monitoring devices, and drones for inspection can make maintenance more efficient. Budgeting for ongoing maintenance ensures the green roof remains a viable and attractive feature of the building. Effective maintenance balances aesthetic appeal with functional performance, keeping the roof system healthy year-round.
Environmental and Urban Impact
Green roof systems play a significant role in enhancing urban environments and promoting sustainability. By mitigating urban heat islands, they help lower surrounding temperatures and reduce energy consumption for cooling. Green roofs also manage stormwater by absorbing rainwater, reducing the load on drainage systems, and minimizing flood risk. These rooftops support urban biodiversity, providing habitats for pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects. They contribute to cleaner air by filtering pollutants and reducing airborne particulates. Green roofs align with sustainable city planning goals, offering eco-friendly alternatives for urban development while enhancing public spaces. In addition, they create educational and community engagement opportunities, encouraging people to connect with nature even in densely populated areas. The widespread adoption of green roofs demonstrates how buildings can actively contribute to environmental conservation and climate resilience.
FAQ
- What is the difference between extensive and intensive green roofs? Extensive green roofs are lightweight, low-maintenance, and typically feature low-growing plants, while intensive green roofs are heavier, support a wide variety of plants, and can resemble full rooftop gardens.
- How much does it cost to install a green roof system? Costs vary depending on roof size, materials, plant selection, and labor, but investing in a green roof can reduce long-term energy and maintenance expenses.
- Can green roofs be installed on any type of building? Most buildings can accommodate green roofs, but a structural assessment is essential to ensure the roof can bear additional weight.
- How long does a green roof last with proper maintenance? With regular care, a green roof system can last 20 to 50 years or more, depending on materials and environmental conditions.
- What plants are best suited for a green roof system? Sedums, grasses, herbs, and drought-tolerant perennials are popular choices, with plant selection tailored to climate and roof type.
- Do green roofs require irrigation in all climates? Irrigation needs depend on local rainfall, plant type, and roof design; some extensive green roofs may require minimal watering.
- How do green roofs help with energy efficiency? Green roofs provide insulation, reduce heat absorption, and lower cooling costs by moderating temperature fluctuations on roof surfaces.
Takeaway
A green roof system is more than a visually appealing addition to a building; it is an investment in sustainability, urban health, and long-term economic benefits. By carefully designing, installing, and maintaining these systems, property owners can create functional green spaces that reduce energy consumption, manage stormwater, and support biodiversity. With increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for climate-resilient urban infrastructure, green roofs offer a practical and effective solution. Whether for residential, commercial, or municipal buildings, adopting a green roof system demonstrates a commitment to ecological stewardship while enhancing the quality of life for urban communities.