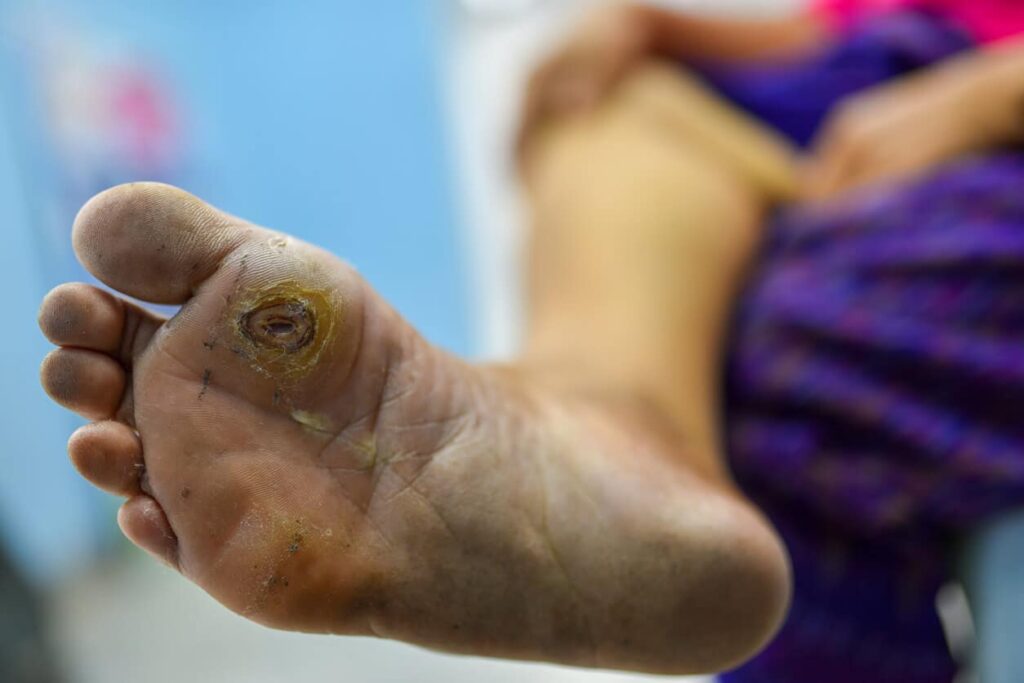
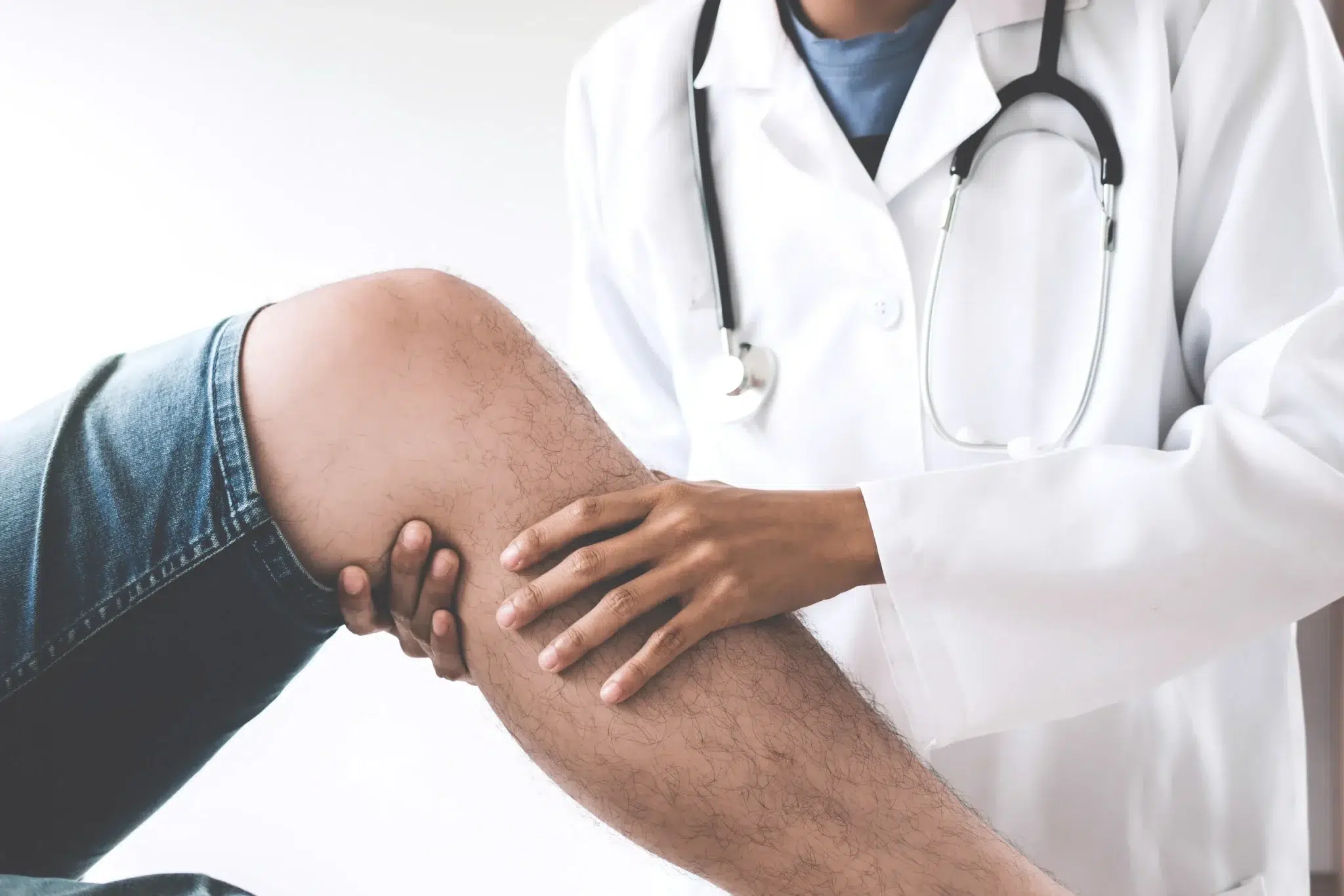
Diabetic gangrene is one of the most serious complications that can arise when diabetes is not managed properly. It occurs when high blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves, reducing blood flow to extremities, especially the feet and toes. Without proper circulation, wounds do not heal and infections thrive, leading to dead or decaying tissue known as gangrene. This condition can quickly escalate from a small sore or ulcer into a life-threatening medical problem if left untreated. Orthopedic specialists play an important role in managing diabetic gangrene because bones, joints, and surrounding tissues are often affected. Their expertise helps determine whether a limb can be preserved through surgery and advanced wound care or whether more drastic interventions are needed. By understanding how orthopedics fits into diabetic care, patients and families can appreciate the value of timely medical attention.
Common Signs and Risks Associated with Diabetic Gangrene
Diabetic gangrene often begins subtly, which makes awareness of early symptoms essential for diabetic patients. Discoloration of the skin, ranging from pale to black, is one of the most recognizable signs. Patients may also notice numbness due to nerve damage or experience pain, swelling, and foul-smelling discharge from infected wounds. The feet and lower legs are most vulnerable because they endure pressure and reduced circulation. Risk factors such as poor foot hygiene, wearing tight footwear, uncontrolled blood sugar, smoking, and peripheral vascular disease increase the likelihood of developing gangrene. What may start as a small blister can deteriorate into tissue death if overlooked. Orthopedic specialists emphasize early recognition of these symptoms so that surgical and medical interventions can be applied before complications worsen. Awareness of these risks allows patients to take proactive measures to protect their limbs.
Orthopedic Evaluation for Diabetic Gangrene
When diabetic gangrene is suspected, an orthopedic evaluation is a critical step in the treatment process. Physicians begin by conducting a physical examination, carefully assessing the appearance of the affected area and determining the extent of tissue damage. Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, are often ordered to check whether the infection has spread into the bones, a condition called osteomyelitis. Laboratory tests, including cultures and blood work, help identify the type of bacteria involved and guide antibiotic therapy. Orthopedic surgeons also evaluate whether the gangrene is dry or wet, as the treatment plan can differ significantly between the two. They often collaborate with endocrinologists, vascular surgeons, and wound care specialists to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the patient’s condition. Timely evaluation not only prevents complications but also increases the chances of saving the limb. Patients who undergo orthopedic assessments early typically experience better recovery outcomes.
Orthopedic Treatment Approaches for Diabetic Gangrene
Orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene involves a range of medical and surgical strategies depending on the severity of the case. Surgical debridement is often the first step, where infected and dead tissue is removed to prevent the spread of infection and allow healthy tissue to recover. In cases where the infection reaches the bones, orthopedic surgeons manage the condition with procedures designed to stabilize and preserve as much healthy bone as possible. Reconstructive surgery may also be performed to restore function and support long-term mobility. Amputation, although considered a last resort, becomes necessary when the infection is too extensive to control. Even in such cases, orthopedic surgeons focus on ensuring that patients can recover with the aid of prosthetics and rehabilitation. Advanced wound care techniques, such as negative pressure wound therapy and specialized dressings, are used to promote healing. Each approach aims to give patients the best chance at recovery while reducing the risk of recurrence.
Role of Technology and Innovation in Orthopedic Treatment
Modern technology has transformed how orthopedic specialists manage diabetic gangrene. Advanced imaging tools now allow surgeons to accurately map tissue damage and plan precise surgical interventions. Techniques such as minimally invasive debridement reduce recovery times and lower the risk of complications. Specialized orthopedic implants can provide structural stability when infection compromises bone strength. Innovative wound care systems, including negative pressure wound therapy, create controlled environments that speed up healing. Prosthetic technology has also advanced significantly, providing diabetic patients who undergo amputations with more functional and comfortable solutions. Rehabilitation programs now integrate virtual therapy and computer-assisted training to help patients regain mobility more effectively. These innovations not only improve survival rates but also enhance overall quality of life. Orthopedic specialists are at the forefront of applying these technologies to give diabetic patients renewed confidence and independence after severe complications.
Preventive Orthopedic Care for Diabetic Patients
Preventive care plays a vital role in reducing the risk of diabetic gangrene. Orthopedic specialists often encourage patients with diabetes to undergo routine foot and joint evaluations to catch small issues before they become severe. Custom orthotics and specialized footwear are recommended to relieve pressure points that could develop into ulcers. Education on daily foot hygiene, careful inspection of toes and soles, and prompt reporting of wounds or blisters help patients stay vigilant. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining controlled blood sugar levels, exercising to improve circulation, and quitting smoking, further lower the risk. Orthopedic involvement at an early stage often prevents complications from reaching the point of gangrene. By focusing on prevention, patients not only avoid costly and painful procedures but also enjoy a healthier quality of life. Proactive orthopedic care is a cornerstone of diabetic management that provides peace of mind and long-term benefits.
Recovery and Rehabilitation in Orthopedic Care
Recovering from orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene requires patience, persistence, and medical guidance. After surgery, careful infection control is critical to ensure that wounds heal properly and do not return. Physical therapy helps patients regain strength, balance, and mobility, especially if reconstructive surgery or amputation has been performed. Pain management techniques are integrated into recovery plans to reduce discomfort while allowing patients to stay active. Rehabilitation also focuses on psychological support, as the emotional impact of gangrene and limb loss can be overwhelming for patients and families. Orthopedic teams work closely with rehabilitation specialists to provide training in mobility aids and prosthetics where needed. Long-term follow-ups with orthopedic care ensure that patients remain on track and any complications are addressed early. Recovery is a continuous process, but with proper guidance, patients can adapt, regain independence, and return to fulfilling daily activities.
FAQ Section
Q1: Why is orthopedic treatment necessary for diabetic gangrene?
Orthopedic treatment is necessary because gangrene often affects bones and joints, requiring specialized surgical interventions. Orthopedic specialists assess whether the limb can be preserved and provide targeted procedures that focus on saving healthy tissue. Their expertise ensures a structured approach to both limb preservation and functional recovery.
Q2: Can orthopedic treatment always prevent amputation?
Amputation is not always avoidable, especially when infection spreads too far. However, orthopedic treatment significantly improves the chances of saving the limb when intervention occurs early. Even if amputation is required, orthopedic surgeons make sure patients are prepared for recovery with prosthetic support and rehabilitation strategies.
Q3: What surgical options do orthopedic doctors use for diabetic gangrene?
Orthopedic doctors use procedures such as debridement to remove dead tissue, reconstructive surgery to restore stability, and in severe cases, amputation to prevent the spread of infection. Each option is carefully chosen based on the patient’s overall condition and the extent of the damage.
Q4: How can diabetic patients reduce the risk of gangrene?
Patients can lower risks by maintaining stable blood sugar levels, practicing daily foot care, wearing protective footwear, and avoiding smoking. Regular checkups with orthopedic specialists and timely treatment of small wounds prevent them from progressing into gangrene. Preventive care combined with lifestyle changes is the most effective way to stay safe.
Q5: What role does rehabilitation play after orthopedic surgery for gangrene?
Rehabilitation helps patients regain mobility, build strength, and adapt to lifestyle changes following surgery. It includes physical therapy, pain management, emotional support, and long-term monitoring by orthopedic specialists. Proper rehabilitation ensures that patients recover as fully as possible and reduce the chance of recurring complications.