Understanding the Scope of General Orthopedics
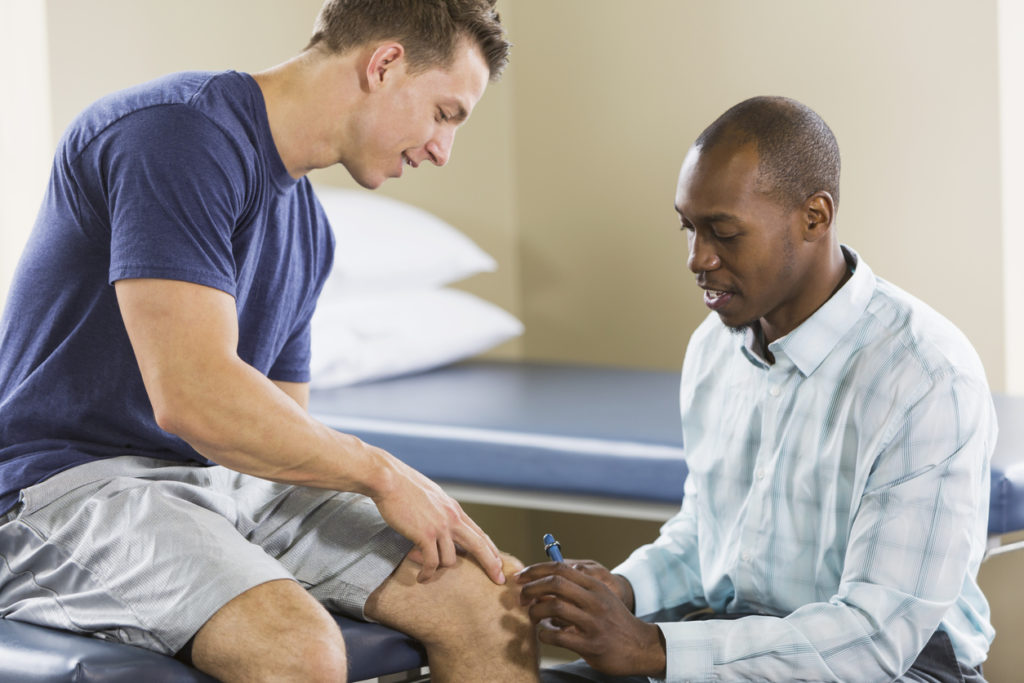
General Orthopedics focuses on diagnosing and treating conditions that affect the bones, joints, ligaments, muscles, and tendons. It plays a vital role in maintaining mobility and ensuring people can perform everyday activities without discomfort or limitations. This field covers a wide range of non-surgical and surgical treatments designed to restore strength, reduce pain, and improve overall function. Many individuals seek orthopedic care when they experience persistent pain, swelling, reduced range of motion, or injuries from accidents or physical activities. General orthopedic providers help evaluate these concerns using advanced diagnostic tools and personalized care strategies. As healthcare evolves, orthopedic medicine continues to expand with better technology, improved treatment methods, and more accurate imaging. This growth allows patients to access high-quality care that supports long-term musculoskeletal health.
Conditions Commonly Treated in General Orthopedics
Joint and Bone Disorders
General orthopedists commonly treat joint and bone concerns that interfere with movement and daily comfort. Arthritis is one of the most widespread conditions, affecting millions of people with symptoms such as stiffness and inflammation. Joint instability can develop from injury or age-related degeneration, often causing pain during routine tasks. Bone alignment issues are also frequently addressed, especially when they contribute to uneven pressure on joints or long-term mobility limitations. These conditions often progress slowly, making early evaluation important for preventing worsening discomfort. Orthopedic specialists assess joint and bone health through physical exams and imaging tests to determine appropriate treatments. Their care helps patients regain comfort and confidence in their everyday activities.
Acute and Overuse Injuries
Acute injuries such as sprains and strains often bring patients to orthopedic clinics because they cause sudden pain and functional limitations. Ligament injuries are also common, especially in athletes or individuals with physically active lifestyles. Repetitive strain injuries are another key concern because they gradually develop from overuse, improper movement patterns, or repetitive work tasks. Stress fractures frequently occur when bones face excessive pressure without enough time to recover. These injuries can significantly disrupt routines, making early evaluation essential for proper healing. Orthopedic specialists help determine the severity of each injury and develop individualized treatment plans. Timely intervention can reduce long-term damage and support healthier recovery.
Age-Related Orthopedic Concerns
Older adults face unique orthopedic concerns due to natural wear and tear on the musculoskeletal system. Degenerative joint changes, such as those seen in osteoarthritis, can lead to persistent discomfort that limits mobility. Osteoporosis increases the risk of fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist. Reduced muscle mass also contributes to decreased balance, which raises the likelihood of falls. General Orthopedics helps address these concerns using preventive care, strength-building exercises, and treatments that support bone health. Many older adults benefit from personalized guidance to maintain independence and quality of life. Early awareness and proactive management play a major role in preventing serious injuries.
Pediatric Orthopedic Issues
Children and adolescents often require orthopedic care due to rapid growth and increased physical activity levels. Growth plate injuries are common because these areas of developing bone are more vulnerable to trauma. Developmental abnormalities affecting bones or joints may also require long-term monitoring and treatment. Young athletes frequently experience sports-related injuries, including muscle strains, sprains, and fractures. Orthopedic specialists offer careful assessments to protect growing bones and ensure proper development. Parents often seek orthopedic guidance when children complain of persistent pain or difficulty with certain movements. Early attention helps prevent complications and encourages healthy development.
Diagnostic Approaches in General Orthopedics
Orthopedic care heavily relies on accurate diagnostics to pinpoint the source of pain or dysfunction. Physical examinations help evaluate strength, flexibility, balance, and range of motion to narrow down possible conditions. Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds provide detailed visuals of the bones, joints, and soft tissues. Laboratory tests may be used when inflammation, infection, or systemic issues are suspected as underlying causes. Advanced imaging becomes necessary when symptoms are complex or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. Early diagnosis is crucial because it leads to targeted treatment and reduces the risk of complications. Patients benefit from a clear understanding of their condition, which helps them take an active role in their care plan.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options in General Orthopedics
Medications
Medication plays a vital role in managing pain and inflammation associated with orthopedic conditions. Over-the-counter pain relievers are commonly used for mild to moderate discomfort. In more severe cases, prescription medications may help reduce inflammation or support healing. Steroid injections are an option when localized inflammation requires targeted relief. Bone health medications can be recommended for individuals at risk for osteoporosis. These medications are often combined with lifestyle changes and physical therapy to maximize effectiveness. Patients receive guidance on safe usage and potential side effects to ensure proper management.
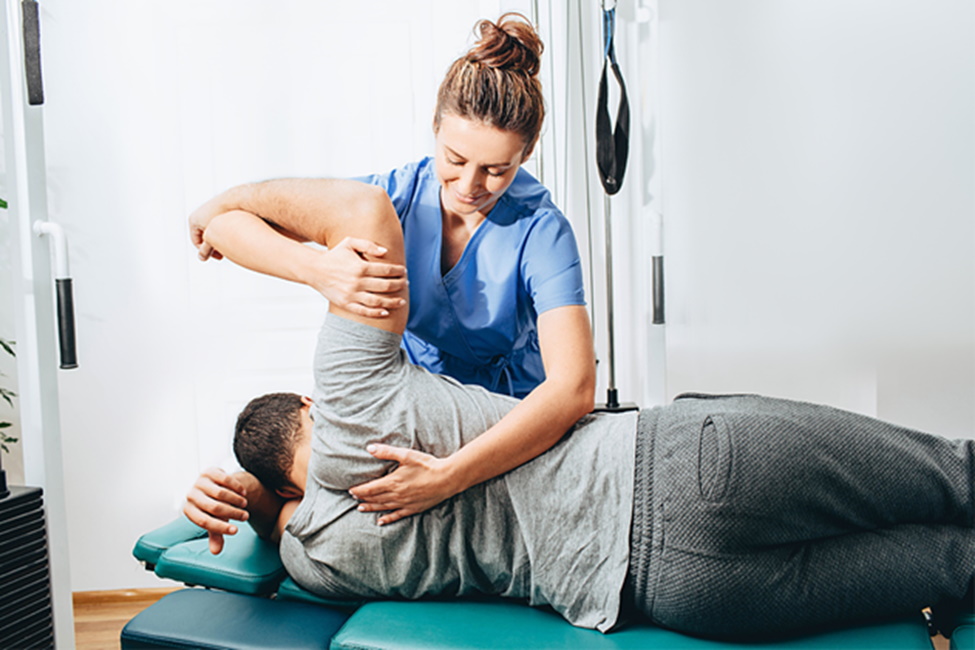
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of orthopedic recovery and long-term musculoskeletal wellness. Therapists design personalized programs that strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore movement. Many rehabilitation plans include techniques such as stretching, resistance training, and manual therapy. Certain modalities like heat, cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation further support recovery. Physical therapy helps reduce pain, prevent future injuries, and improve overall function. Regular sessions encourage consistency, which is essential for long-term improvement. Patients who follow their rehabilitation plans often see significant gains in mobility and comfort.
Lifestyle and Activity Modifications
Adjusting daily habits can greatly influence orthopedic health and boost recovery. Ergonomic changes at home or work can reduce strain on joints and muscles. Many people benefit from learning proper movement mechanics to avoid unnecessary stress on the body. Regular exercise helps strengthen key muscle groups that support the joints. Weight management is also important because it reduces pressure on weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips. Patients are encouraged to incorporate low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. These simple changes play a substantial role in reducing pain and preventing injuries.
Assistive Devices
Assistive devices provide additional support during healing and help individuals move with greater ease. Braces and orthotics help stabilize joints and correct alignment issues. Slings and supportive wraps may be used temporarily after injury or surgery. Mobility aids such as canes and walkers help individuals maintain independence while reducing the risk of falls. Using these devices properly enhances safety and allows the body to recover more efficiently. Orthopedic specialists guide patients on selecting and using the right equipment. These tools contribute to improved confidence and mobility during treatment.
Surgical Options in General Orthopedics
When Surgery Becomes an Option
Surgery becomes necessary when conservative treatments no longer provide adequate relief or when structural damage is too severe. Orthopedic specialists evaluate each patient’s condition carefully to determine whether surgery is the best path forward. Persistent pain, instability, or reduced mobility often indicate a need for surgical intervention. Surgeons explain the risks, benefits, and expected recovery process to help patients make informed decisions. Many orthopedic conditions respond very well to surgery, especially with modern techniques that minimize tissue disruption. Patients who undergo surgery often experience significant improvements in function. Clear communication and careful planning ensure better surgical outcomes.
Common Orthopedic Surgeries
General orthopedists perform a wide range of surgeries designed to restore function and reduce pain. Joint replacement surgeries for the hip, knee, and shoulder are among the most common procedures. Arthroscopic surgeries allow surgeons to repair injuries using small incisions and specialized cameras. Fracture fixation techniques using plates, screws, and pins help bones heal in proper alignment. Soft tissue repairs such as tendon and ligament reconstruction also fall within orthopedic care. These procedures help patients regain mobility and return to their daily activities. Ongoing follow-up ensures that healing progresses as expected.
Advancements in Orthopedic Surgical Techniques
Technological advancements have significantly improved orthopedic surgery. Robotic-assisted surgery enhances precision and reduces recovery time for many patients. New implant materials offer greater durability and better compatibility with the human body. Minimally invasive techniques reduce scarring, discomfort, and downtime. Modern anesthesia methods also make procedures safer and more comfortable. Recovery programs have evolved to include early mobility strategies that support faster healing. These advancements offer patients greater confidence in the safety and effectiveness of surgical care.
Preventive Orthopedic Care for Long-Term Musculoskeletal Health
Strength and Flexibility Training
Maintaining strong muscles is essential for supporting joints and preventing injuries. Regular strengthening exercises help stabilize the spine, hips, and knees. Flexibility training keeps muscles mobile and less prone to strain. Balanced routines that combine stretching and strengthening provide the best results. Many people benefit from working with fitness professionals or physical therapists for guidance. Implementing these practices into weekly habits supports long-term orthopedic health. Prevention through proper conditioning often reduces the need for more extensive treatment later.
Safe Athletic Practices
Athletes and active individuals must prioritize safe practices to avoid injuries. Proper warm-ups prepare muscles for activity and reduce strain. Cool-down sessions help maintain flexibility and reduce soreness. Sport-specific techniques and training improve performance while minimizing risk. Adequate rest is important to prevent overuse injuries. These approaches help maintain strong, functional bodies capable of handling physical demands. Individuals who practice safe exercise habits tend to experience fewer long-term orthopedic problems.
Bone Health Maintenance
Bone health is essential for preventing fractures and maintaining mobility. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D helps support strong bones. Supplements may be recommended for individuals with deficiencies. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking or light resistance training stimulate bone strength. Fall prevention strategies become especially important with age. Regular checkups allow orthopedic specialists to monitor bone density and recommend personalized care. These habits help preserve skeletal strength throughout life.
Workplace and Daily Life Ergonomics
Proper body mechanics can prevent many orthopedic issues. Simple changes in desk setup can greatly reduce strain on the neck and back. Learning how to lift heavy items safely protects the spine. Taking frequent breaks during repetitive tasks helps prevent overuse injuries. Ergonomic tools, supportive chairs, and proper posture contribute to overall comfort. Individuals who implement ergonomic principles often experience fewer injuries and less chronic pain. These adjustments create a healthier environment at home and work.
The Role of a General Orthopedist in Ongoing Patient Care
General orthopedists guide patients through diagnosis, treatment, recovery, and long-term wellness. They coordinate with primary care providers and specialists when necessary. Patients with chronic conditions receive consistent monitoring and adjustments to their care plan. Orthopedic providers support shared decision-making to ensure patients understand their options. Their comprehensive approach addresses both immediate needs and long-term health. Ongoing support encourages patients to stay engaged in their treatment. This partnership helps individuals achieve better outcomes and maintain active lifestyles.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Provider
Selecting the right orthopedic provider is an important step in achieving effective care. Patients should look for board-certified specialists with extensive experience. Many people also prefer practices that offer imaging, therapy, and surgery in one location. During an appointment, patients can ask questions about diagnosis, treatment options, and expected results. A strong patient-provider relationship improves communication and trust. Providers who take time to explain conditions clearly help patients feel more confident. Comfort, expertise, and accessibility all play key roles in choosing a provider. This careful selection promotes a better healthcare experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What symptoms should prompt a visit to a general orthopedist
Persistent pain, swelling, reduced mobility, and difficulty performing daily activities are common reasons to seek care.
Can orthopedic issues heal without surgery
Yes, many conditions respond well to non-surgical treatments such as therapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications.
Are orthopedic treatments safe for older adults
Most treatments are safe and highly beneficial when tailored to the patient’s health and activity level.
Do I need a referral to see a general orthopedic specialist
Many clinics accept self-referrals, but some insurance plans require authorization.
How long does recovery typically take for orthopedic conditions
Recovery varies depending on the severity of the condition and the chosen treatment, but timely care leads to better outcomes.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent orthopedic problems
Regular exercise, proper ergonomics, balanced nutrition, and maintaining a healthy weight contribute to long-term orthopedic health.
Takeaway
General Orthopedics plays an essential role in diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. With a wide range of non-surgical and surgical options, it supports individuals of all ages in maintaining mobility, strength, and comfort. Early attention, proper diagnostics, and preventive care can greatly improve long-term outcomes. Patients who stay engaged with their orthopedic health experience better function and improved quality of life. Whether managing an injury, addressing chronic discomfort, or seeking preventive guidance, orthopedic care provides valuable support. Taking proactive steps today helps protect bone and joint health for years to come.