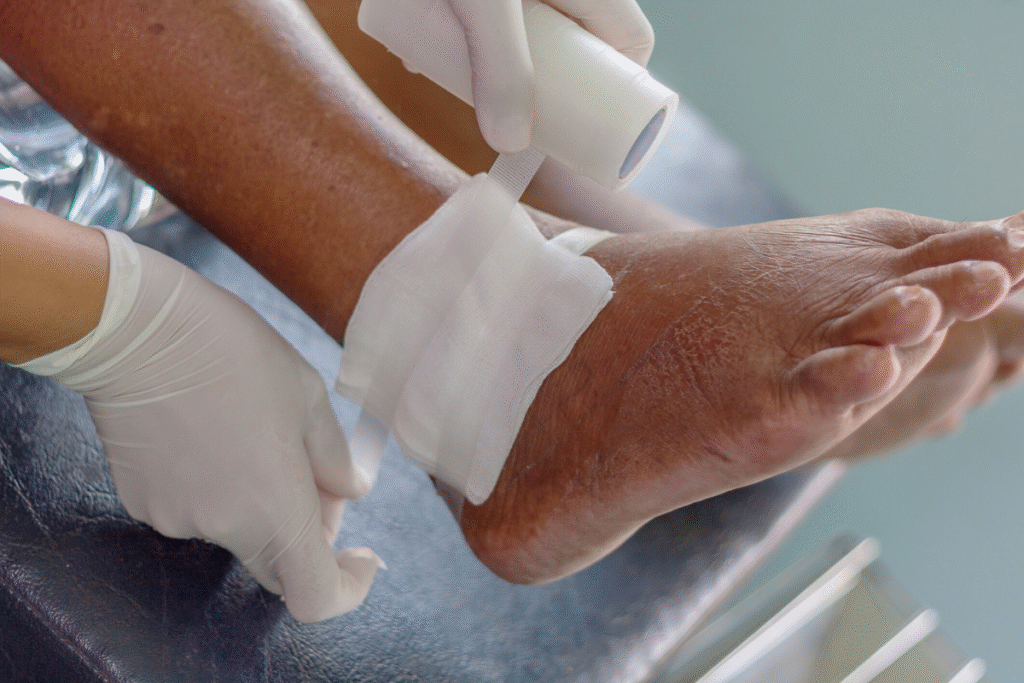
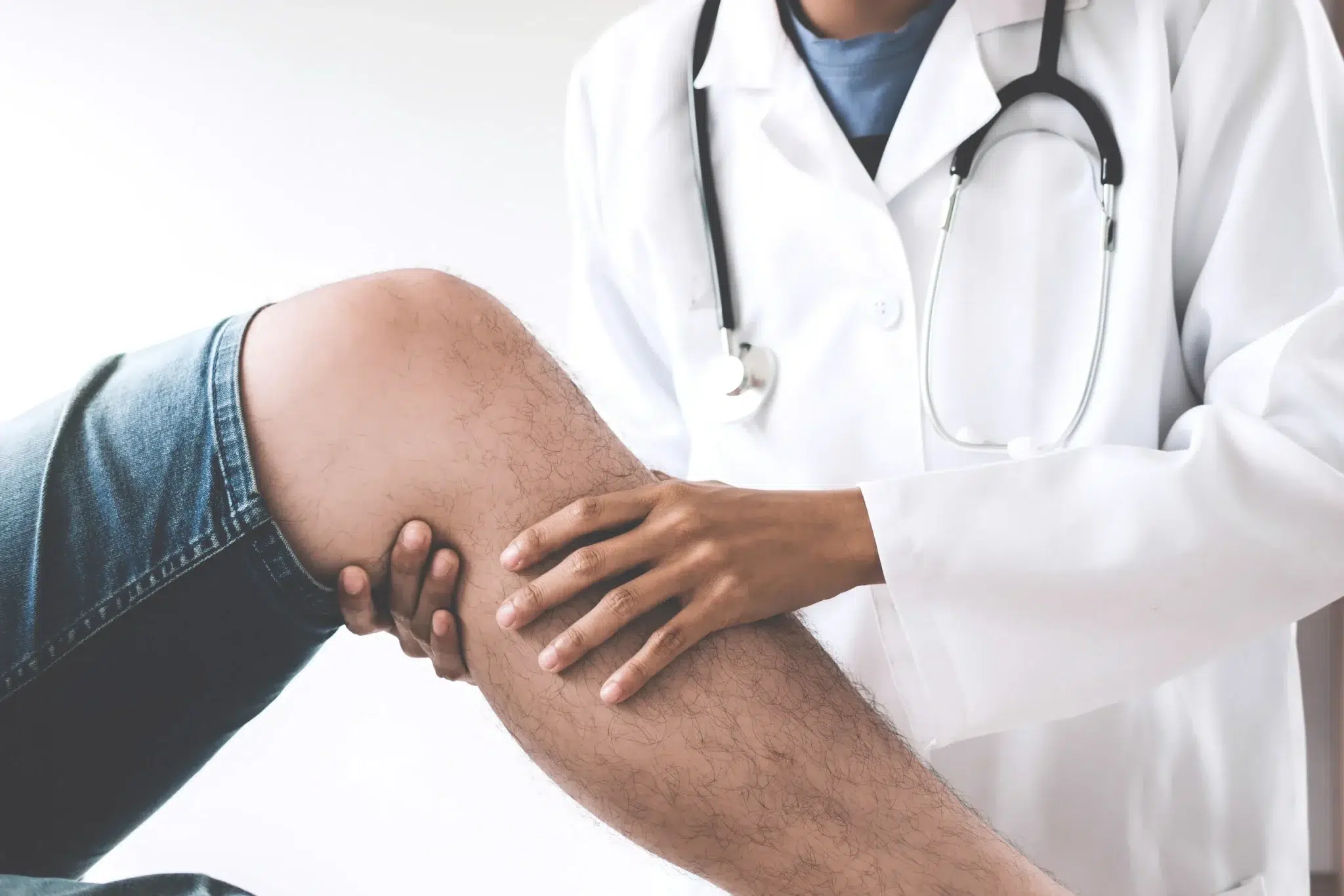
Non-healing wounds, often referred to as chronic wounds, are injuries that fail to progress through the normal stages of healing within a typical timeframe, usually 4 to 6 weeks. These wounds can be painful, frustrating, and sometimes dangerous if left untreated. Common causes include diabetes, vascular insufficiency, infections, pressure ulcers, or trauma that damages underlying tissues. Orthopedic factors can play a significant role in delayed healing, particularly when there is compromised bone health, poor joint stability, or structural deformities that increase pressure on the wound site. Understanding the root cause is essential, as addressing only the surface wound without considering musculoskeletal contributions may result in recurring or worsening conditions. Patients often experience swelling, redness, discharge, or limited mobility as the wound persists. Orthopedic specialists offer a unique perspective in treating these wounds, targeting both the injury and the underlying skeletal or soft tissue issues to promote complete recovery.
Understanding the Role of Orthopedic Care in Wound Healing
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds goes beyond surface-level care, focusing on how the musculoskeletal system affects recovery. Specialists assess bone alignment, joint stability, and tissue support to determine how these factors impact wound healing. For instance, pressure on a bony prominence can lead to chronic ulcers, especially in diabetic or immobile patients. Correcting these underlying problems through orthopedic interventions can significantly improve healing outcomes. Orthopedic physicians often collaborate with wound care nurses, physical therapists, and other medical professionals to ensure a comprehensive approach. Addressing structural issues such as foot deformities, poor gait mechanics, or joint misalignment can reduce repeated trauma to the wound site. Additionally, orthopedic care emphasizes improving circulation and mobility, which are critical components of tissue regeneration. This holistic approach helps prevent recurring wounds and supports long-term recovery.
Diagnostic Approaches in Orthopedic Wound Treatment
Proper diagnosis is essential for effective orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Imaging techniques like X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans allow doctors to assess bone health, detect hidden infections, and evaluate soft tissue damage. Laboratory tests may be conducted to check for infection, inflammation, or nutritional deficiencies that could slow healing. Assessing blood flow is crucial, especially for patients with diabetes or peripheral arterial disease, as poor circulation can prevent the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to the wound. Orthopedic specialists also examine the mechanical factors contributing to the wound, such as abnormal pressure points, misaligned bones, or limited joint mobility. These evaluations guide the treatment plan, ensuring that interventions target both the wound and the underlying issues preventing healing. Regular monitoring allows for adjustments in therapy, which improves the likelihood of a positive outcome. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in diagnostic discussions to better understand their treatment pathway.
Treatment Options Offered by Orthopedic Specialists
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds includes a combination of surgical and non-surgical approaches tailored to the patient’s needs. Debridement, or the removal of dead and infected tissue, is often the first step to prepare the wound for healing. Surgical interventions may include bone stabilization, corrective procedures, or soft tissue reconstruction to address underlying musculoskeletal problems. Advanced wound dressings and negative pressure therapy can help promote tissue regeneration while minimizing infection risk. Antibiotic therapy is commonly used to control bacterial infections that may hinder healing. Orthopedic specialists also emphasize optimizing blood flow and reducing pressure on the affected area through custom footwear, orthotics, or offloading devices. By addressing both the wound itself and the mechanical or structural contributors, these treatments provide a comprehensive path toward recovery.
Advanced Therapies for Non-Healing Wounds
For wounds that do not respond to conventional methods, orthopedic specialists may employ advanced therapies to stimulate healing. Stem cell therapy has shown promise in promoting tissue regeneration by introducing specialized cells that support repair. Growth factor treatments can accelerate cellular activity and encourage new tissue formation. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is another effective option, delivering high levels of oxygen directly to the wound site to enhance healing, fight infection, and improve circulation. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, derived from the patient’s own blood, are increasingly used to stimulate tissue growth and improve wound closure. These therapies often work best when combined with traditional orthopedic interventions, creating a synergistic effect that enhances recovery. Patients should discuss the suitability and potential outcomes of these treatments with their specialist, as individual factors like age, health conditions, and wound severity influence effectiveness. Advanced therapies offer hope for wounds that have previously resisted conventional care.
Preventive Measures and Rehabilitation
Preventing further complications is an essential part of orthopedic wound management. Offloading pressure from the affected area through specialized footwear, padding, or mobility aids can significantly reduce stress on the wound and encourage healing. Physical therapy plays a key role in restoring movement, improving circulation, and strengthening muscles that support the affected limb. Lifestyle modifications, including proper nutrition, smoking cessation, and blood sugar control, are also critical for wound recovery. Patients with chronic conditions are encouraged to maintain regular follow-up visits to monitor progress and prevent recurrence. Education on proper wound care techniques, early detection of infection, and self-management strategies empowers patients to take an active role in healing. A proactive approach reduces the risk of complications and ensures long-term success in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds.
Monitoring Progress and Follow-Up Care
Regular monitoring is vital to assess the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Specialists document wound size, tissue quality, and signs of infection to determine whether adjustments in therapy are necessary. Follow-up care often includes periodic imaging, lab tests, and physical assessments to track healing progress. Patient adherence to prescribed therapies and lifestyle recommendations is critical for achieving optimal outcomes. Education about recognizing early warning signs of complications, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge, helps prevent worsening conditions. Continuous communication between the patient and healthcare team ensures timely intervention if healing stalls. Effective monitoring not only supports wound recovery but also addresses the underlying orthopedic factors contributing to delayed healing.
Common Challenges in Orthopedic Wound Treatment
Treating non-healing wounds through orthopedic interventions can present several challenges. Chronic conditions like diabetes, vascular disease, or autoimmune disorders may slow healing and complicate treatment plans. Patient compliance is essential, as inconsistent adherence to medication, wound care protocols, or physical therapy can hinder progress. Recurrent infections or delayed bone healing may require additional interventions or extended treatment timelines. Some patients may experience pain, reduced mobility, or emotional distress due to persistent wounds. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach between the patient and the orthopedic care team. By anticipating potential obstacles, specialists can implement preventive strategies and adjust treatments to support successful outcomes.
FAQ
What qualifies as a non-healing wound?
A non-healing wound is one that does not progress through the typical stages of healing within 4 to 6 weeks, often showing persistent tissue damage, infection, or inflammation.
When should I consult an orthopedic specialist?
If a wound fails to heal despite standard care, shows signs of infection, or is associated with bone or joint issues, consulting an orthopedic specialist can help identify underlying causes.
Are surgical options always necessary?
Not all patients require surgery. Many non-surgical interventions, including advanced dressings, offloading, and physical therapy, can be effective depending on the wound and patient condition.
How long does it take for non-healing wounds to improve with orthopedic care?
Healing time varies based on wound severity, underlying conditions, and patient compliance. Some wounds may show improvement within weeks, while others may require months of treatment.
Can non-surgical therapies be effective on their own?
Yes, non-surgical therapies like advanced wound dressings, hyperbaric oxygen, PRP injections, and physical therapy can support healing, especially when combined with lifestyle modifications and proper monitoring.